Exploring the World of Asset Management Jobs: Opportunities, Roles, and Career Paths
In today’s dynamic financial landscape, asset management jobs offer a diverse array of opportunities for finance professionals seeking rewarding careers. The asset management industry plays a pivotal role in managing investments, making it a critical component of the broader financial services sector. This article will provide an in-depth exploration of asset management jobs, shedding light on the roles, responsibilities, career paths, and the promising future that this field holds for professionals seeking to make their mark in finance.
The Essence of Asset Management Jobs
Asset management is the practice of overseeing a pool of investments on behalf of clients, with the primary goal of optimizing returns while managing risk. Asset managers, also known as portfolio managers, work diligently to make investment decisions that align with clients’ financial objectives and risk tolerance. The industry encompasses various asset classes, including equities, fixed income, real estate, and alternative investments.
Types of Asset Management Jobs
The world of asset management offers a diverse range of job opportunities, each catering to different skill sets, interests, and career goals. Let’s explore some of the key roles within this dynamic field:
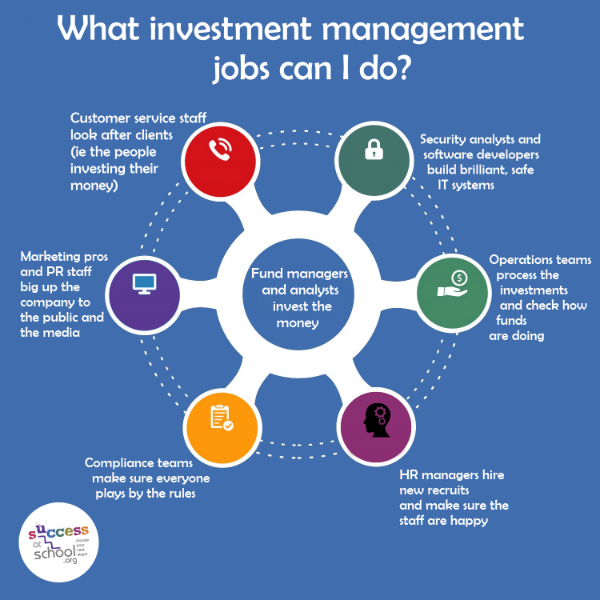
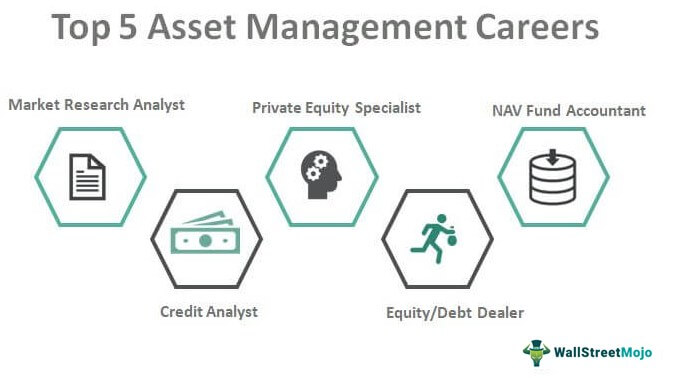
- Portfolio Manager: Portfolio managers are responsible for making investment decisions on behalf of clients or investment funds. They analyze market trends, evaluate securities, and construct portfolios that align with specific investment objectives.
- Research Analyst: Research analysts conduct in-depth analysis of financial markets, industries, and individual securities. They provide valuable insights and recommendations to portfolio managers for investment decisions.
- Client Relationship Manager: Client relationship managers, also known as client portfolio managers, serve as the bridge between clients and the asset management firm. They understand clients’ needs, communicate investment strategies, and ensure client satisfaction.
- Risk Manager: Risk managers focus on identifying and mitigating risks within investment portfolios. They use quantitative models and risk assessment tools to safeguard clients’ assets.
- Fund Operations Specialist: Fund operations specialists oversee the day-to-day administrative and operational aspects of investment funds. They ensure compliance with regulations, manage fund accounting, and facilitate fund transactions.
- Sales and Marketing: Sales and marketing professionals are responsible for promoting asset management services to clients. They build relationships, create marketing campaigns, and play a critical role in attracting new clients.
- Compliance Officer: Compliance officers ensure that the asset management firm operates within regulatory guidelines and complies with industry standards. They monitor and assess regulatory risks, implement compliance policies, and conduct audits.
Key Skills and Qualities for Asset Management Jobs
Professionals pursuing careers in asset management should possess a blend of technical expertise and personal qualities to excel in this demanding field. Some essential skills and qualities include:
- Analytical Skills: Asset management professionals must be adept at analyzing financial data, market trends, and investment opportunities to make informed decisions.
- Communication Skills: Effective communication is vital, as professionals interact with clients, colleagues, and stakeholders. Clear communication ensures that investment strategies are well-understood and aligned with client goals.
- Quantitative Aptitude: Many asset management roles require proficiency in quantitative analysis and modeling to assess risk and evaluate investment opportunities.
- Attention to Detail: Asset managers must pay close attention to detail to avoid errors in portfolio construction and risk management.
- Adaptability: The financial landscape is constantly evolving. Asset management professionals should be adaptable and willing to learn about new investment products, technologies, and strategies.
- Ethical Conduct: Integrity and ethical conduct are paramount, as asset managers handle clients’ financial assets and must uphold the highest ethical standards.
Career Paths in Asset Management
The career paths within asset management are diverse, offering opportunities for professionals at various stages of their careers. Let’s explore some common career progression paths:
- Entry-Level Positions: Many professionals start their asset management careers as research analysts, fund operations specialists, or junior portfolio managers. These roles provide foundational experience in financial analysis and operations.
- Mid-Level Positions: With experience, individuals can progress to roles such as portfolio manager, senior research analyst, or client relationship manager. These positions involve more significant responsibilities and client interaction.
- Senior Management: Seasoned professionals may ascend to senior management roles, including Chief Investment Officer (CIO), Chief Compliance Officer (CCO), or Chief Executive Officer (CEO) of asset management firms.
- Specialization: Asset managers often have the opportunity to specialize in specific asset classes, such as equities, fixed income, or alternative investments. Specialization can lead to roles like equity strategist, fixed income portfolio manager, or hedge fund manager.
- Entrepreneurship: Some experienced asset managers choose to start their own investment firms, becoming entrepreneurs and managing their funds or advisory businesses.
The Promising Future of Asset Management Jobs
The outlook for asset management jobs remains promising. As individuals and institutions continue to seek professional guidance for their investments, the demand for asset management services is expected to grow. Factors contributing to this growth include:
- Demographic Trends: An aging population seeking retirement planning and wealth management services is driving demand for asset management expertise.
- Wealth Accumulation: As economies grow, individuals accumulate wealth, creating the need for professional asset management to optimize investment returns.
- Globalization: Asset managers are increasingly managing global portfolios, necessitating expertise in international markets and investments.
- Technological Advancements: The integration of technology, including artificial intelligence and data analytics, is enhancing investment decision-making and expanding the scope of asset management.
- Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) Investing: The rise of ESG investing reflects the growing importance of ethical and sustainable investment practices, creating new opportunities within asset management.
Conclusion
Asset management jobs offer diverse and rewarding career opportunities for finance professionals. Whether you aspire to become a portfolio manager, research analyst, or client relationship manager, the asset management industry provides a platform for individuals to leverage their skills and expertise to help clients achieve their financial goals. As the demand for professional asset management services continues to grow, the future looks promising for those embarking on or advancing in their asset management careers. Whether in a bustling financial hub or a smaller community, asset management remains a dynamic and influential field within the finance industry, shaping the financial futures of individuals and organizations alike.